I remember the first time I realized how a dash of titanium dioxide could completely transform ceramics.
Titanium dioxide (TiO₂) breathes life into ceramics by amplifying color brilliance, increasing opacity, and boosting mechanical strength thanks to its unique optical and chemical properties. Essential in glaze formulations, it creates brighter finishes and enhances thermal stability.
Imagine holding a piece of ceramic that’s not just beautiful but also strong enough to withstand the test of time. That’s what TiO₂ does—it doesn’t just make ceramics prettier; it makes them tougher. I learned this firsthand when working on a project where the ceramics needed to endure both beauty and resilience, and TiO₂ was the secret ingredient that made it all possible. Its ability to create vivid colors and intricate patterns while ensuring durability makes it indispensable in ceramics production. Whether it’s the sheen of a vase or the robustness of a tile, TiO₂ ensures that each piece isn’t just visually appealing but also built to last.
[claim claim=”Titanium dioxide enhances ceramic color vividness.” istrue=”true” explanation=”TiO₂ improves ceramics’ color through its unique optical properties.”]
[claim claim=”TiO₂ decreases the thermal stability of ceramics.” istrue=”false” explanation=”TiO₂ actually contributes to the thermal stability of ceramics.”]
How Does TiO₂ Influence Color and Opacity in Ceramic Glazes?
Ever wondered how that beautiful, glossy finish on your favorite ceramic mug comes to life?
TiO₂ in ceramic glazes increases opacity and color brightness by scattering light due to its high refractive index. This results in vivid colors and diverse surface textures.
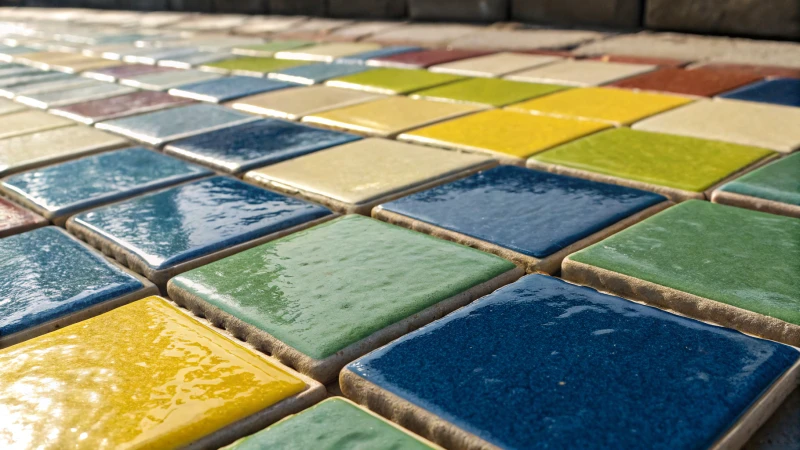

The Science Behind TiO₂’s Optical Properties
Imagine standing in front of a painting, where each brushstroke transforms with the light. That’s kind of what titanium dioxide does in ceramic glazes. It has this amazing ability to scatter light, thanks to its high refractive index, which means it makes colors pop—like they’re singing right back at you! I remember the first time I saw a glaze with TiO₂ at work; it was like someone had turned up the volume on color itself, bringing out hues that ranged from gentle pastels to bold, vibrant shades.
In ceramics, TiO₂ is the magician behind the curtain, working as an opacifier. It diffuses light, hiding the raw clay underneath, which is key when you want the glaze’s true colors to shine without any interference from what’s below.
| Property | Effect on Glaze |
|---|---|
| High Refractive Index | Enhances brightness |
| Strong Scattering Ability | Increases opacity |
Interaction with Other Components
Mixing TiO₂ with different metal oxides is like creating a symphony of colors. I once experimented by combining it with iron oxides and was amazed by the array of earthy tones it produced. Pairing it with cobalt oxides? The blues were so striking; they reminded me of a clear summer sky. These experiments showed me just how versatile TiO₂ particles1 can be in creating variegated patterns2 and complex hues.
During firing, TiO₂ encourages the formation of crystalline phases within the glaze. These crystals not only add texture but also boost mechanical strength and surface durability—qualities any ceramic artist would appreciate.
Practical Applications in Ceramics
For those like me who love tinkering with materials, experimenting with TiO₂ concentrations is part of the joy of ceramics. Adjusting the amount can lead to different visual effects, turning glazes from translucent whispers to opaque statements. It’s this kind of experimentation that makes ceramics such an exciting and dynamic art form.
If you’re eager to dive into TiO₂’s potential, it’s essential to grasp how changing its concentration alters glaze properties. A slight tweak might yield minor shifts, but a significant adjustment could completely transform both color and texture.
Understanding these interactions has helped me push boundaries and achieve new results in my work through innovative techniques3. This knowledge is especially valuable for those looking to refine their craft or develop fresh products for the market.
[claim claim=”TiO₂ enhances opacity in ceramic glazes.” istrue=”true” explanation=”TiO₂’s high refractive index and light scattering ability increase glaze opacity.”]
[claim claim=”TiO₂ cannot produce blue hues in ceramics.” istrue=”false” explanation=”When combined with cobalt oxides, TiO₂ can yield vibrant blue colors.”]
How Does Titanium Dioxide Boost Ceramic Durability?
Ever wonder how a simple ingredient can transform ceramics into something incredibly durable and versatile?
Titanium dioxide (TiO₂) boosts ceramic durability by enhancing mechanical strength, thermal stability, and optical properties. It forms crystalline phases and alters electrical attributes, contributing to advanced functionalities and sustainability in ceramics.

The Chemistry Behind TiO₂ in Ceramics
I remember the first time I stumbled upon the magic of titanium dioxide (TiO₂) while working on a ceramics project. It was like discovering a secret ingredient that could turn ordinary clay into a masterpiece. This little powerhouse enhances mechanical properties by forming crystalline phases4 that toughen up the ceramics, making them resistant to cracks and breaks. The way TiO₂ interacts with other oxides to form titanate compounds is nothing short of fascinating, as it alters electrical characteristics, opening up new possibilities for advanced ceramics.
Optical and Aesthetic Enhancements
Have you ever admired the vibrant colors and intricate patterns on a ceramic piece and wondered what makes them so captivating? That’s often TiO₂ at work, thanks to its high refractive index. It brings out bright colors and creates stunning finishes. I once worked on a glaze that needed that extra pop, and TiO₂ did the trick by adding depth and opacity, creating breathtaking variegated patterns that were as much art as they were science.
Thermal Stability and Durability
I can still recall the intense heat of the kiln during my first ceramic firing session. The ability of TiO₂ to provide thermal stability is crucial here. It helps ceramics withstand high temperatures without losing their shape or integrity, which is vital for many applications. Plus, by allowing for lower-temperature vitrification, it helps save on energy costs—something that aligns perfectly with our collective push towards sustainability.
Application Examples
| Application | Role of TiO₂ |
|---|---|
| Glazing | Enhances color, opacity |
| Advanced ceramics | Modifies electrical properties |
| Sustainable ceramics | Lowers energy needs in firing |
Innovations with Nano-TiO₂
The future of ceramics is evolving with innovations like nano-TiO₂. I’ve seen how it fine-tunes microstructures and boosts hardness, enabling precise control over sintering processes. This opens doors to multifunctional ceramics5, blending traditional uses with groundbreaking applications across industries.
Opportunities for Further Research
Every time I dive into research about TiO₂, I find new ways it can revolutionize ceramic engineering. Doping TiO₂ with different elements holds the promise of unlocking new functionalities like catalytic and antimicrobial properties. As we push for high-performance ceramics, exploring TiO₂-based solutions6 will be key to future advancements.
In my journey through the world of ceramics, titanium dioxide has proven itself indispensable, merging durability, aesthetics, and functionality in ways that continuously redefine what’s possible in ceramic engineering.
[claim claim=”TiO₂ enhances ceramic fracture resistance.” istrue=”true” explanation=”TiO₂ forms crystalline phases that improve toughness and fracture resistance.”]
[claim claim=”TiO₂ decreases the optical properties of ceramics.” istrue=”false” explanation=”TiO₂ has a high refractive index, enhancing color and opacity in ceramics.”]
Can Titanium Dioxide Improve Ceramic Thermal Stability?
Ever wondered how something as simple as titanium dioxide can transform ceramics into high-temperature warriors?
Absolutely! Titanium dioxide significantly boosts ceramic thermal stability. It serves as a flux agent, aids in forming crystalline phases, and enhances mechanical strength, allowing ceramics to endure extreme heat while maintaining their form.

Understanding Titanium Dioxide’s Role
When I first learned about titanium dioxide (TiO₂), I was amazed by its versatility, especially in enhancing the thermal stability7 of ceramics. It’s not just about making things heat-resistant; it’s about transforming the very essence of the material.
Chemical Interactions
Think of TiO₂ as the unsung hero that collaborates with other oxides to create titanate compounds. These compounds are crucial for thermal stability and also modify electrical properties, boosting the material’s durability. The innovations in nano-TiO₂8 further enhance these processes, which I find incredibly fascinating.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
I remember working on a project where the integrity of ceramics was a major concern. Thanks to TiO₂, we achieved remarkable mechanical strength through the formation of crystalline phases. Here’s a quick snapshot of its impact:
| Property | Influence of TiO₂ |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Enhanced |
| Fracture Toughness | Increased |
| Sintering Control | Improved |
Environmental Benefits
From an environmental standpoint, TiO₂ lowers the energy needed during firing by reducing vitrification temperatures. This aligns perfectly with sustainability goals and environmental protection9, making it a win-win.
Advanced Functionalities
Research into TiO₂ doping has unlocked potential for advanced functionalities like catalytic and antimicrobial properties. Imagine ceramics that are not just structurally sound but also capable of catalytic functions10. It’s a game-changer!
Exploring titanium dioxide’s role is like piecing together a puzzle where every piece contributes to the elegance and resilience of ceramics in high-stakes environments.
[claim claim=”TiO₂ improves ceramic thermal stability.” istrue=”true” explanation=”TiO₂ enhances thermal stability by forming titanate compounds, increasing durability.”]
[claim claim=”TiO₂ increases ceramic sintering temperatures.” istrue=”false” explanation=”TiO₂ actually lowers vitrification temperatures, reducing energy consumption.”]
How does TiO₂ revolutionize advanced ceramic applications?
Have you ever wondered how a simple compound like titanium dioxide could transform the world of ceramics?
TiO₂ is crucial in ceramics for its role as a flux agent, color developer, and enhancer of mechanical strength. It forms titanate compounds, essential for electrical properties and durability in advanced ceramics.

The Role of TiO₂ in Color Development
I remember the first time I saw the incredible colors achieved in ceramic art, and it was like magic. It turns out, TiO₂ is the secret ingredient behind those vibrant hues and opaque glazes. Thanks to its high refractive index, it scatters light like nobody’s business, giving ceramic artists11 the power to create stunning visual effects by just tweaking the glaze formulation. Imagine painting with light itself!
Enhancing Mechanical Properties
I once had a ceramics instructor who emphasized the importance of strength in pottery. TiO₂ comes into play here by forming crystalline phases that bolster the mechanical strength of ceramics. This process is akin to giving your creations a backbone, improving fracture toughness and making them more durable. For instance, nano-TiO₂ fine-tunes microstructures, helping us control sintering processes12 with precision.
Electrical Properties Modification
The interaction of TiO₂ with other oxides is fascinating—it forms titanate compounds that modify electrical properties. This is essential for piezoelectric or dielectric applications where electrical functionalities13 are key. It’s like giving ceramics a new superpower!
| Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High Refractive Index | Enhances color and opacity |
| Crystalline Phases | Improves mechanical strength |
| Titanate Formation | Modifies electrical properties |
Thermal Stability and Sustainability
TiO₂ doesn’t just stop at making things beautiful and strong; it also enhances thermal stability. It ensures ceramics maintain their structure even under high temperatures and promotes lower-temperature vitrification. This means less energy used during firing—a win for sustainability goals14. I always think about how every little bit helps when we talk about sustainability.
Innovations in TiO₂ Applications
Innovation never stops with TiO₂. Researchers are exploring doping it with elements to unlock new properties like antimicrobial effects. These breakthroughs are paving the way for multifunctional ceramic systems, maximizing resource efficiency and opening doors to new possibilities.
With its versatility, TiO₂ is more than just an additive; it’s a game-changer in the world of advanced ceramics, driving ongoing technological advancements15 that keep us on the edge of our seats.
[claim claim=”TiO₂ enhances color in ceramic glazes.” istrue=”true” explanation=”TiO₂’s high refractive index scatters light, creating vibrant colors.”]
[claim claim=”TiO₂ reduces ceramics’ mechanical strength.” istrue=”false” explanation=”TiO₂ forms crystalline phases that enhance mechanical strength.”]
Conclusion
Titanium dioxide (TiO₂) enhances ceramics by improving color brilliance, opacity, and mechanical strength, making them more durable and visually appealing while also promoting thermal stability.
-
Discover how titanium dioxide’s refractive properties enhance color brightness in ceramic glazes. ↩
-
Explore how different metal oxides interact with TiO₂ to create unique glaze patterns. ↩
-
Learn about new techniques that utilize TiO₂ to achieve exciting results in ceramics. ↩
-
Understand how crystalline phases formed by TiO₂ enhance the mechanical strength of ceramics. ↩
-
Explore how multifunctional ceramics utilize TiO₂ to offer diverse applications across industries. ↩
-
Learn about innovative uses of TiO₂ in enhancing ceramic durability and functionality. ↩
-
Learn about TiO₂’s role in enhancing ceramic heat resistance, crucial for high-temperature applications. ↩
-
Explore how advancements in nano-TiO₂ optimize ceramic properties like hardness and toughness. ↩
-
Understand how TiO₂ contributes to eco-friendly ceramics through energy-efficient processes. ↩
-
Discover how doping TiO₂ introduces new properties like antimicrobial and catalytic effects. ↩
-
Discover how TiO₂ transforms ceramic glaze colors by enhancing brightness and opacity through its scattering properties. ↩
-
Understand the impact of nano-TiO₂ on fine-tuning microstructures and controlling sintering processes. ↩
-
Explore the formation of titanate compounds and their effect on ceramics’ piezoelectric applications. ↩
-
Learn about TiO₂’s role in reducing energy consumption through low-temperature vitrification. ↩
-
Stay updated with cutting-edge innovations involving TiO₂, including its doped forms for new functionalities. ↩